The Value of Using a LoZ Meter in Circuit Diagnostics
In the realm of circuit diagnostics, the Low Impedance (LoZ) meter has become an indispensable tool for technicians. Unlike traditional high-impedance meters, LoZ meters introduce a deliberate load to the circuit during voltage measurements, offering a more accurate representation of the circuit's health.
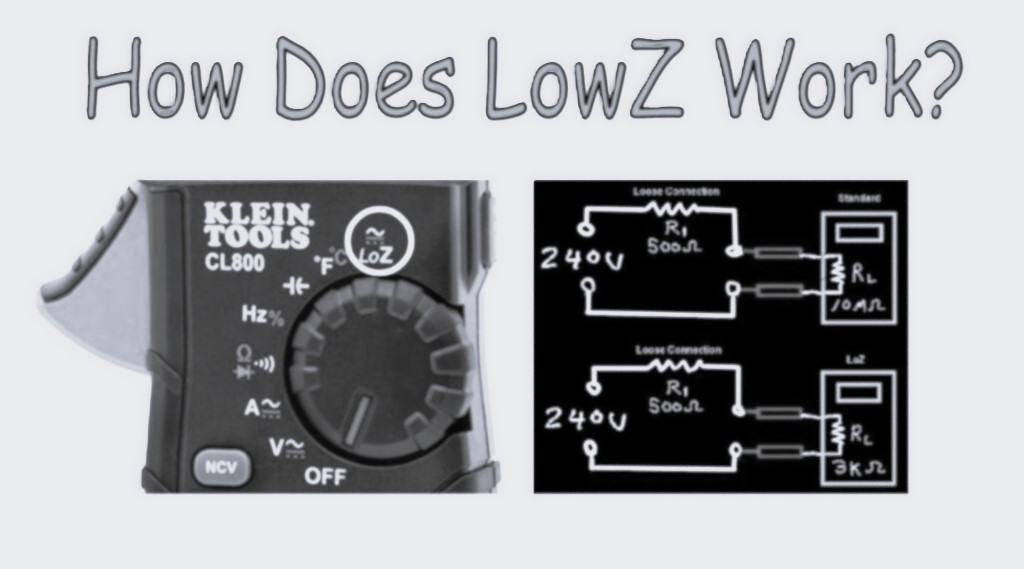
Understanding LoZ Meters
Traditional digital multimeters (DMMs) typically have high input impedance, often around 10 megaohms. While this design minimizes circuit loading, it can inadvertently detect "ghost voltages." These phantom readings result from capacitive coupling or electromagnetic induction, especially in environments with multiple live conductors in close proximity. Such misleading voltages can lead technicians astray during diagnostics.
LoZ meters address this issue by incorporating a lower input impedance, approximately 3,000 ohms. This intentional loading dissipates ghost voltages, ensuring that only genuine voltage readings are displayed. For instance, the Klein CL800, a popular LoZ meter, utilizes a thermistor to achieve this low impedance, enhancing measurement accuracy.
Advantages in Circuit Diagnostics
1. Eliminating Ghost Voltages
By applying a load to the circuit, LoZ meters effectively neutralize ghost voltages, preventing false readings and ensuring technicians focus on actual electrical issues.2. Identifying Compromised Voltage Sources
LoZ meters can detect voltage drops caused by high-impedance connections, such as loose wiring. In scenarios where a traditional meter might display a full voltage reading despite a compromised connection, a LoZ meter reveals the voltage drop, indicating potential issues.3. Enhanced Safety
Accurate voltage readings are crucial for technician safety. By providing reliable measurements, LoZ meters help prevent misdiagnoses that could lead to hazardous situations.Practical Application Example
Consider an electric dryer that operates but fails to produce heat. A traditional high-impedance meter might read the expected 240V across the heating element, suggesting no issues. However, using a LoZ meter forces any upstream loose connections to pass more current than a traditional meter would. This causes a greater voltage loss across the loose connection, resulting in a reduced voltage reading at the meter, such as 205V. This discrepancy directs the technician to investigate further, revealing said loose connection that impedes proper current flow.
Limitations and Considerations
While LoZ meters are invaluable in many diagnostic scenarios, they are not universally applicable. Introducing a low impedance load can affect circuits with high-impedance components, potentially altering their operation or causing damage. Therefore, technicians should exercise caution and understand when LoZ measurements are appropriate.
Conclusion
Incorporating a LoZ meter into circuit diagnostics enhances measurement accuracy by eliminating ghost voltages and identifying compromised connections. Technicians equipped with this tool can diagnose electrical issues more effectively, ensuring both the reliability of their assessments and their personal safety. As with any diagnostic instrument, understanding its proper application is key to maximizing its benefits.
For a comprehensive understanding of LoZ meters and their applications, resources like The Tech Circuit offer in-depth insights and practical examples.
Please see this video on why using a LoZ meter is so important: https://youtu.be/lIX5AtdEJOs

